This is a theme I’ve explored a few times in the past: the NPS results for sports teams.
Despite an imperious performance by the Shannonsiders in last weekend’s All-Ireland Hurling Final, Limerick’s Net Promoter score is only +7.
The Greatest Final in Modern Times?
On Sunday, we witnessed one of the greatest hurling matches of the modern era. Hurling, you ask? A game played with sticks and a small hard ball called a sliotar. The greatest, fastest, most skillful game in the world. It truly is.
I should declare an allegiance here. Even though Deep-Insight is headquartered in Cork, I was born in Limerick. Although I didn’t live in the county for very long, I do support the Shannonsiders whenever it gets to the business end of an All-Ireland Hurling championship.
Last Sunday was All-Ireland Final day and it was a contest between the two best teams in the country: Limerick and Cork. It turned out to be a game of men against minnows as Limerick bullied and outplayed Cork into submission in an enthralling display of hurling. The final score: Limerick 3-32 to Cork’s 1-22.
Limerick Player Ratings
Here’s Paul Keane’s full list of Limerick player ratings from this week’s Irish Examiner:
Nickie Quaid: Not much he could do about Shane Kingston’s early bullet that flew past him to the net. Kept a clean sheet thereafter and mixed up his puck-outs well, going short when the opportunities were there. 8 (‘Passive’ score in NPS terminology)
Sean Finn: Beaten by Shane Kingston for the Cork goal. Started on Jack O’Connor though switched over to Patrick Horgan for a period. Horgan took him for two points from play but both were serious efforts from the Cork captain. 8 (Passive)
Dan Morrissey: Expected to pick up Patrick Horgan and did so for the most part, holding the prolific forward scoreless from play in that time. Locked down a mean defence that had to deal with an early Cork whirlwind. 8 (Passive)
Barry Nash: Punched the air in delight after closing out the first-half scoring with a long-range point. Still there at the death, attempting to tag on one last score for the Shannonsiders. 8 (Passive)
Diarmaid Byrnes: At his very best again. It was Byrnes’ precise pass that created Aaron Gillane’s goal and he split the posts for a trademark long-range point approaching half-time. Denied Seamus Harnedy a goal with a 64th-minute block. 8 (Passive)
Declan Hannon: Another textbook display at the centre of the Limerick defence. Used all his leadership to nail the quarterback role. Helped get Limerick going with an early point from distance and finished with 0-2. Hobbled off to a huge ovation late on. 8 (Passive)
Kyle Hayes: None of the drama of the Munster final when he scored the goal of the season but still worked tirelessly, winning frees and shooting for points long after the result was beyond doubt. 7 (Passive)
William O’Donoghue: A big part of why Limerick got on top in the middle third. Emptied his tank and strung together the play intelligently. 7 (Passive)
Darragh O’Donovan: On point and crisp at midfield, delivering accurate passes throughout and thundering through the exchanges. One of 13 different Limerick players to get on the scoresheet on the day. 8 (Passive)
Gearóid Hegarty: A huge performance from the reigning Hurler of the Year. Clipped 2-2 and struck two wides in the first half alone as he opened up with some spectacular hurling. Eventually replaced to huge cheers. 8 (Passive)
Cian Lynch: Pointed after 11 seconds and never let up, setting up both of Gearóid Hegarty’s goals. Toyed with the Cork defence at times, finishing with six points from play. His interception and flick up for Tom Morrissey’s 18th-minute point was outrageous. 9 (Promoter)
Tom Morrissey: Mixed silk with steel, showing an awesome work rate but also an ability to pick off a series of deft passes that led to important scores. Weighed in with three points from play himself on another landmark day. 8 (Passive)
Aaron Gillane: Hard to believe now he didn’t start the Munster final. Looked like a player keen to prove a point and was on fire throughout, finishing with the first-half with 1-3 and adding another three points for a 1-6 haul. 8 (Passive)
Seamus Flanagan: Helped put the game beyond Cork during Limerick’s early blitzkrieg, pointing sumptuously in the eighth minute and passing to Aaron Gillane for the second goal. Scored just a point but set up so much more. 8 (Passive)
Peter Casey: A bittersweet afternoon for the Na Piarsaigh man. Clear to play after his red card in the semi-final and on fire for 30 minutes, shooting 0-5 from play. Then crumpled with a left knee injury and had to come off. 8 (Passive)
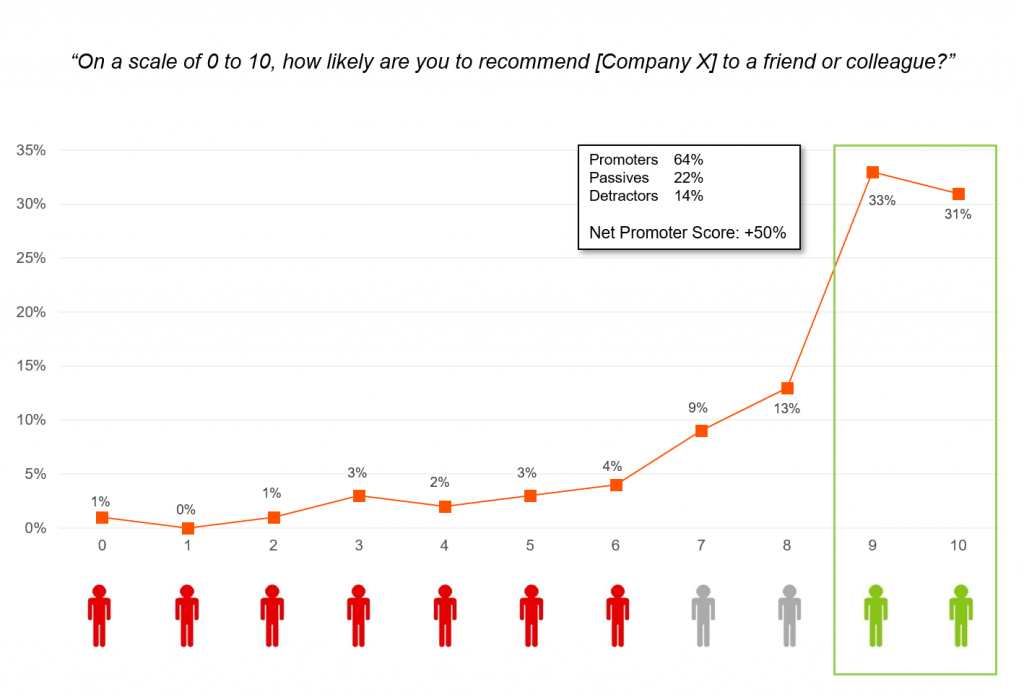
Limerick’s Net Promoter score is only +7
The best ranking player was Cian Lynch who strode the field like a Colossus but who was the only player to get 9/10 from the Irish Examiner correspondent.
15 players and only one achieved a score consistent with a ‘Promoter’ ranking of 9 or 10; Everybody else was a Passive, in a match where Limerick utterly dominated their Munster rivals and played one of the most memorable matches in living memory.
Net Promoter Score = % of Promoters (7%) less % of Detractors (0%), hence a Net Promoter Score of +7.
Benchmarking
I have written before about how benchmarking needs to be conducted carefully when you compare scores from customers in different countries.
I have also written about how people in different countries are culturally programmed to score in particular ways. The most obvious example is that Americans are more prone to score more positively than Europeans if they receive a good service.
This is an important point to remember if you are running a Customer Experience (CX) programme across a global client base. An average Net Promoter score for Northern European B2B companies is no higher than +10. For American companies, it’s more like +20 or +30, a score that would be regarded as ‘excellent’ in a Northern European context.
So be careful when comparing NPS results across different jurisdictions. If it helps, just remember that Limerick’s Net Promoter score is only +7 in a year where they dominated the All-Ireland hurling final!
UPDATE (17 July 2022 All-Ireland Final)
Yesterday, Limerick won the All-Ireland Hurling Final again. This time they defeated Kilkenny in another enthralling battle that ended 1-31 to 2-26.
Sadly, their Net Promoter Score was -13. Yes, MINUS 13, according to Conor McKeon of The Independent:
Nickie Quaid – 7
Seán Finn – 7
Mike Casey – 7
Barry Nash – 8
Diarmaid Byrnes – 9
Declan Hannon – 8
Dan Morrissey – 6
Wiliam O’Donoghue – 6
Darragh O’Donovan – 6
Gearóid Hegarty – 9
Kyle Hayes – 8
Tom Morrissey – 8
Aaron Gillane – 7
Séamus Flanagan – 7
Graeme Mulcahy – 5